Drawing graphics programmatically is a very popular task these days. You can easily solve it using Matplotlib library with Python4Delphi (P4D). P4D is a free set of instruments that allows you to work with Python scripts, modules and types in Delphi. In this post, we will look at how to run Matplotlib library using Python for Delphi.
Delphi itself offers a number of advanced charting libraries. TeeChart is a third party chart bundled with the RAD Studio installation. If you have an existing Python application and you need to create charts you could use the Matplotlib library or you could send the data to Delphi and create the chart there. Alternately, you could create the chart via Matplotlib and then display it in the Delphi Windows GUI app. You can use Python4Delphi a number of different ways such as:
Python Matplotlib library provides various tools for working with 2D graphics. With this library, you can create graphics, customize legends, style sheets, color schemes, and manipulate images. There are examples of code from the Matplotlib below.
 We got acquainted with some of the Matplotlib library’s features. Go here, download this library and draw your beautiful graphs. Download Python4Delphi and build Python GUIs for Windows using Delphi easily.
We got acquainted with some of the Matplotlib library’s features. Go here, download this library and draw your beautiful graphs. Download Python4Delphi and build Python GUIs for Windows using Delphi easily.
- Create a Windows GUI around you existing Python app.
- Add Python scripting to your Delphi Windows apps.
- Add parallel processing to your Python apps through Delphi threads.
- Enhance your speed sensitive Python apps with functions from Delphi for more speed.
|
1 2 3 4 |
procedure TForm1.Button1Click(Sender: TObject); begin PythonEngine1.ExecStrings( Memo1.Lines ); end; |
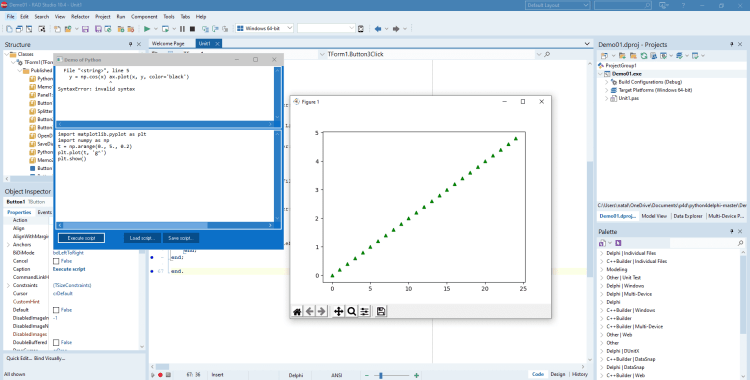
Draw a plot
You can draw very simple plots with Mathplotlib. Or, if you want, you can change the shape and color of the points in the graphic in different ways. In the following example, we will draw the green triangular points using the argument ‘g^’ in function plot().|
1 2 3 4 5 |
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np t = np.arange(0., 5., 0.2) plt.plot(t, 'g^') plt.show() |
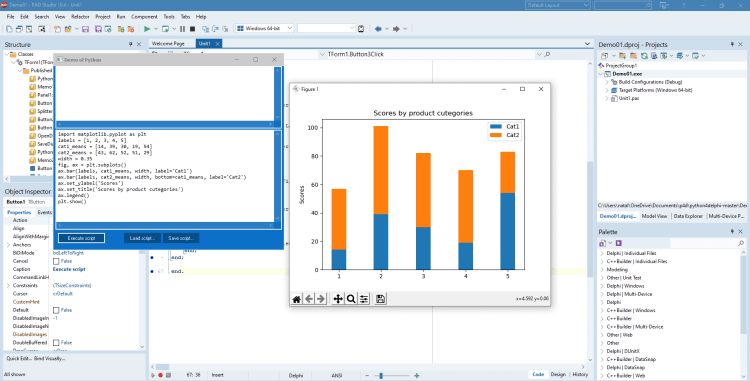
Stacked bar chart
In this example, we show how to draw a stacked bar plot. We will use the function bar() twice. We need to pass to this function such parameters as labels, values of various categories that need to be displayed, names of labels. Finally, we will set such graphic parameters as title, y-label.|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt labels = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] cat1_means = [14, 39, 30, 19, 54] cat2_means = [43, 62, 52, 51, 29] width = 0.35 fig, ax = plt.subplots() ax.bar(labels, cat1_means, width, label='Cat1') ax.bar(labels, cat2_means, width, bottom=cat1_means, label='Cat2') ax.set_ylabel('Scores') ax.set_title('Scores by product cutegories') ax.legend() plt.show() |
Draw curves and fill the area
In this example, we use the function plot() again to build a graphic of cos(x). Then we fill the area in green color between two curves using function fill_between(). Pass parameters x, y1 and y2 to determine the curve and exclude some horizontal regions from being filled using parameter where.|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np fig, ax = plt.subplots() x = np.arange(0, 7 * np.pi, 0.1) y = np.cos(x) ax.plot(x, y, color='black') ax.fill_between(x, 0, 1, where=y > 0.75, color='green', alpha=0.5, transform=ax.get_xaxis_transform()) plt.show() |
 We got acquainted with some of the Matplotlib library’s features. Go here, download this library and draw your beautiful graphs. Download Python4Delphi and build Python GUIs for Windows using Delphi easily.
We got acquainted with some of the Matplotlib library’s features. Go here, download this library and draw your beautiful graphs. Download Python4Delphi and build Python GUIs for Windows using Delphi easily.Reduce development time and get to market faster with RAD Studio, Delphi, or C++Builder.
Design. Code. Compile. Deploy.
Start Free Trial Upgrade Today
Free Delphi Community Edition Free C++Builder Community Edition
Design. Code. Compile. Deploy.
Start Free Trial Upgrade Today
Free Delphi Community Edition Free C++Builder Community Edition